[Main Page](../index.html "Main Page")
# Unifi Switching Lab
The goals of this exercise are:
- Learn how to configure VLANs in a Unifi environment.
- Create VLANs that will be used to segregate wireless traffic.
## About the Environment
In a traditional network environment, you will configure all of the switches individually, or you will use automation tools like Ansible to push a template out to switches.
Unifi provides a web interface where a single configuration is decided, and automatically applied to all of the devices in the network.
## Configuring the Controller
All configuration of the controller is done through the settings dialogue. It's accessed by clicking the gear icon at the lower-left hand of the screen.

## Changing the Default Network
Unifi controllers are installed with a Default "Corporate" network type called LAN. We'll change this network to reflect how we're using it. Click the edit button to start:

- Change the Name to "Management Network"
- Change the "Gateway/Subnet" to match your group's gateway. Group 7 would be 192.168.107.254/24
- Set the DHCP Mode to "None"
- Enable DHCP Guarding, with a Trusted DHCP server of your grou's gateway.
## Adding Standard VLANs
In the Unifi controller, VLANs are types of networks. Add them through the "Networks" dialogue.

Standard VLANs are straightforward. Choose the "VLAN Only" option for purpose, and you'll see you have fewer options to consider now. Two you could enable are IGMP Snooping and DHCP Guarding. IGMP Snooping can help the performance of devices on a network that's receiving multicast traffic. DHCP Guarding ensures that only authorised DHCP servers will be able to offer DHCP leases to devices on the network.

Create three standard VLAN networks with the following attributes:
- Faculty, VLAN 1001, DHCP Guarding with server 10.100.1.1
- Student, VLAN 1002, DHCP Guarding with server 10.100.2.1
- Infrastructure, VLAN 1004, DHCP Guarding with server 10.100.4.1
## Adding a Guest VLAN
Guest VLANs allow network administrators to restrict traffic between hosts. This is useful in environments where un-trusted devices are attached to the network. It also helps to prevent hacking and the spread of viruses between users of a wireless network.

Create a guest VLAN with the following attributes:
- Name: guest
- Purpose: Guest
- VLAN: 1003
- Gateway/Subnet: 10.100.3.1/24
- DHCP Mode: None
- Enable DHCP Guarding, with 10.100.3.1 as a Trusted DHCP server
## Finishing Up
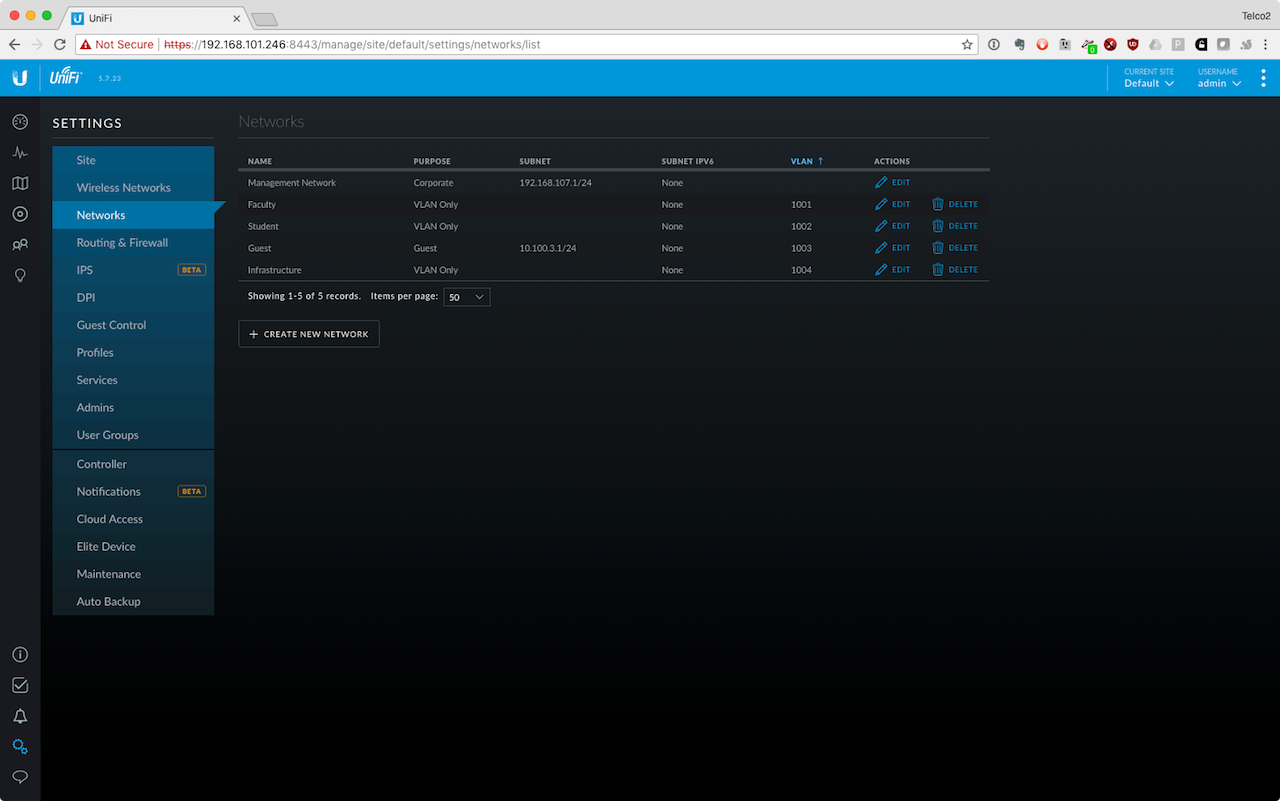
When you've finished configuring your network, it should look like the image below: