This document describes the IP address plan we will use for the workshop exercises using the four AS lab topology.
The IPv4 address space used in these exercises is from subnets of 100.64.0.0/10 which is an IPv4 Shared Address block. It must not be routed on the Internet.
Note that 2001:DB8::/32 is the IPv6 Documentation Address block. It must not be routed on the Internet.
And finally note that the 2001:10::/28 address block has been listed in the IANA special registry for future use. It must not be routed on the Internet.
If using these labs as inspiration for your own infrastructure design, please replace all instances of private, documentation, and unassigned address space with your own address blocks.
The labs that introduce EBGP and implement BGP policies split the physical lab topology into 4 Autonomous Systems. Note the following tables carefully, making sure you are using the correct resources for your router and your AS.
The following table shows the address blocks assigned to each AS:
| AS Number | IPv4 Address block | IPv6 Address block |
|---|---|---|
| 64501 | 100.68.1.0/24 | 2001:DB8:1::/48 |
| 64502 | 100.68.2.0/24 | 2001:DB8:2::/48 |
| 64503 | 100.68.3.0/24 | 2001:DB8:3::/48 |
| 64504 | 100.68.4.0/24 | 2001:DB8:4::/48 |
and from these address blocks we will subdivide as follows:
| AS Number | Function | IPv4 | IPv6 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 64501 | Loopbacks | 100.68.1.248/29 | 2001:DB8:1:0::/64 |
| Point-to-Points | 100.68.1.0/29 | 2001:DB8:1::/56 | |
| 64502 | Loopbacks | 100.68.2.248/29 | 2001:DB8:2:0::/64 |
| Point-to-Points | 100.68.2.0/29 | 2001:DB8:2::/56 | |
| 64503 | Loopbacks | 100.68.3.248/29 | 2001:DB8:3:0::/64 |
| Point-to-Points | 100.68.3.0/29 | 2001:DB8:3::/56 | |
| 64504 | Loopbacks | 100.68.4.248/29 | 2001:DB8:4:0::/64 |
| Point-to-Points | 100.68.4.0/29 | 2001:DB8:4::/56 |
From these high level assignments, we assign the Loopback addresses and the customer subnets used for each router as shown in the following table:
| Router | IPv4 Loopback | IPv6 Loopback | Customer IPv4 Subnet | Customer IPv6 Subnet |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Router1 | 100.68.1.251 | 2001:DB8:1::1 | 100.68.1.32/28 | 2001:DB8:1:100::/56 |
| Router2 | 100.68.1.252 | 2001:DB8:1::2 | 100.68.1.48/28 | 2001:DB8:1:200::/56 |
| Router3 | 100.68.1.253 | 2001:DB8:1::3 | 100.68.1.64/28 | 2001:DB8:1:300::/56 |
| Router4 | 100.68.2.251 | 2001:DB8:2::1 | 100.68.2.32/28 | 2001:DB8:2:100::/56 |
| Router5 | 100.68.2.252 | 2001:DB8:2::2 | 100.68.2.48/28 | 2001:DB8:2:200::/56 |
| Router6 | 100.68.2.253 | 2001:DB8:2::3 | 100.68.2.64/28 | 2001:DB8:2:300::/56 |
| Router7 | 100.68.2.254 | 2001:DB8:2::4 | 100.68.2.80/28 | 2001:DB8:2:400::/56 |
| Router8 | 100.68.3.251 | 2001:DB8:3::1 | 100.68.3.32/28 | 2001:DB8:3:100::/56 |
| Router9 | 100.68.3.252 | 2001:DB8:3::2 | 100.68.3.48/28 | 2001:DB8:3:200::/56 |
| Router10 | 100.68.3.253 | 2001:DB8:3::3 | 100.68.3.64/28 | 2001:DB8:3:300::/56 |
| Router11 | 100.68.4.251 | 2001:DB8:4::1 | 100.68.4.32/28 | 2001:DB8:4:100::/56 |
| Router12 | 100.68.4.252 | 2001:DB8:4::2 | 100.68.4.48/28 | 2001:DB8:4:200::/56 |
| Router13 | 100.68.4.253 | 2001:DB8:4::3 | 100.68.4.64/28 | 2001:DB8:4:300::/56 |
| Router14 | 100.68.4.254 | 2001:DB8:4::4 | 100.68.4.96/28 | 2001:DB8:4:400::/56 |
For the IPv4 loopbacks, we have reserved 100.68.X.248/29; and for the IPv6 loopbacks we have reserved 2001:DB8:X:0::/64, where X is the group number.
IPv6 address space is plentiful and industry practice is to reserve a single /64 for all the loopback interface addresses in the network. IPv4 is very scarce, so we have to be more/very cautious.
Point-to-point links used in operational networks today are addressed as follows (as was covered in the presentations):
IPv4 - a /31 is used for the point-to-point link address (although several network operators are using unnumbered interfaces)
IPv6 - a whole /64 is reserved for the point-to-point link, but the actual assignment itself is a /127 for the link address (and again unnumbered/link-local addressing can be used instead)
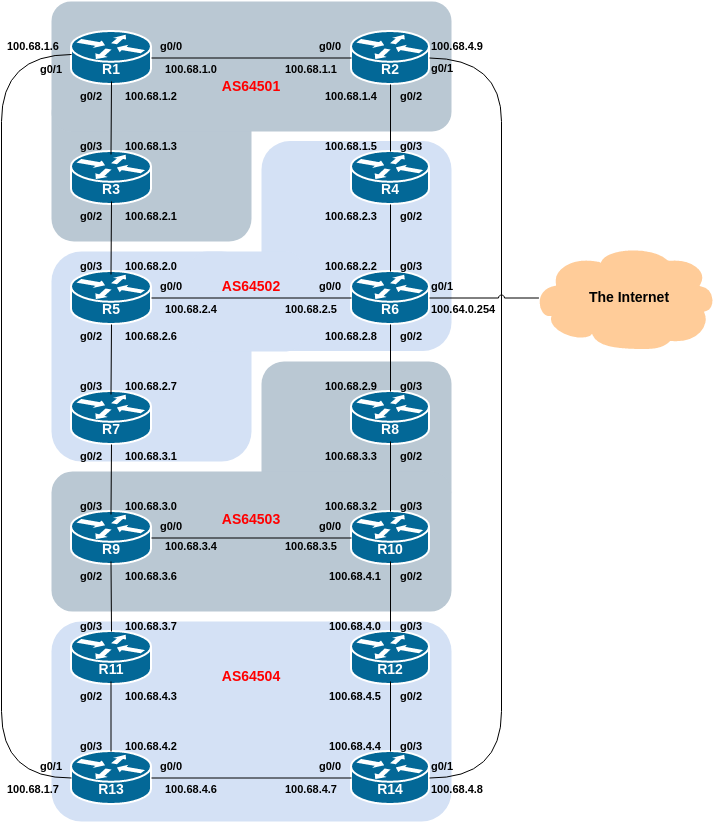
The following diagram shows the IPv4 addressing of the point-to-point links as implemented in the lab topology. Each IPv4 point-to-point link is a /31 subnet.

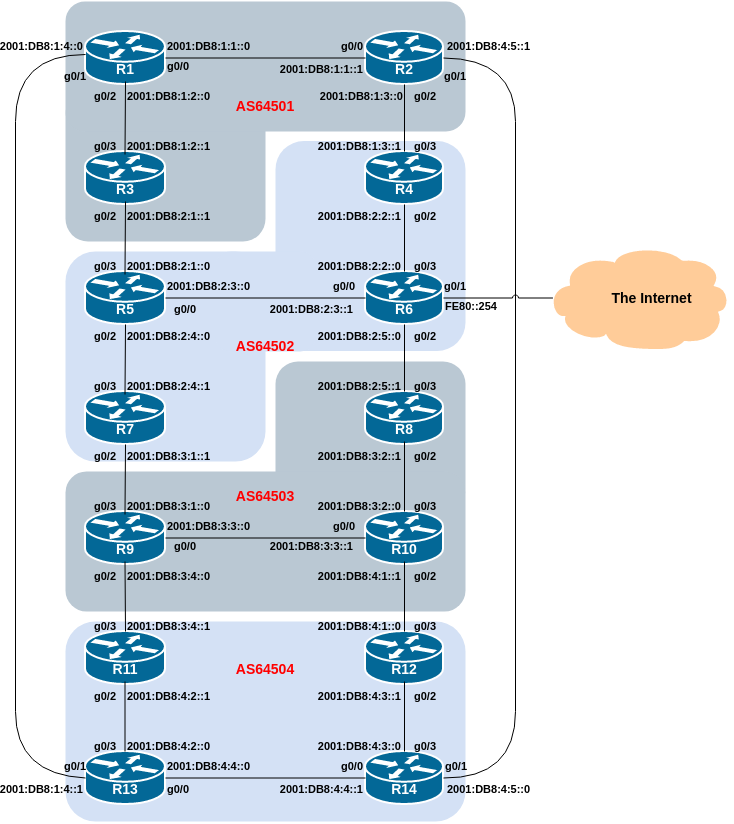
The following diagram shows the IPv6 addressing of the point-to-point links as implemented in the lab topology. Each IPv6 point-to-point link is a /127 subnet out of a /64.